India’s economic growth trajectory has shown signs of deceleration, raising concerns about its underlying dynamics. According to recent reports, the GDP growth in the second quarter of the current fiscal year was recorded at 5.4%, marking the slowest pace in seven quarters. Below, we delve into sectoral performances, investment patterns, and policy implications.
- Sectoral GDP Performance
The sector-wise analysis of GDP growth for 2024 and projected for 2025 reveals notable shifts:
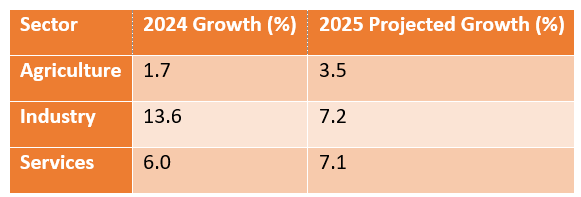
- Agriculture: While growth is projected to rebound to 3.5% in 2025, challenges such as erratic monsoons and inflationary pressures persist.
- Industry: A sharp deceleration is expected in 2025, with growth projected to halve to 7.2%.
- Services: Sustained demand and technological advancements could drive moderate growth in this sector.
- Decline in Investment and Expenditure
The investment trends within the economy show mixed results, indicating cautious optimism amid uncertainty:

The slowdown in private investment, from 11.6% to 5.4%, highlights reduced confidence among investors. Conversely, a slight increase in government spending is anticipated, aiming to spur economic activity.
- Capital Spending Slows Down
Reduced capital spending has impacted infrastructure and industrial growth. Capital expenditure (capex) growth was recorded at 5.1% in 2024 but is expected to drop to 3.0% in 2025. This trend might hinder long-term productivity unless addressed.
- Fiscal Deficit Targets and Policy Responses
The government has set a fiscal deficit target of 4.5% of GDP for 2024-25. While efforts to reduce deficits are commendable, balancing fiscal discipline with growth-oriented spending remains a challenge.
- Decline in Core Industry Growth
Core industries grew at just 3.1% in 2024, reflecting reduced activity in critical sectors such as manufacturing and mining. To reverse this trend, focused policy interventions are necessary to enhance productivity and attract investments.
The report paints a picture of an economy grappling with structural challenges. To sustain long-term growth, a multi-pronged approach focusing on boosting investments, enhancing productivity, and maintaining fiscal discipline is essential. The upcoming budget will be pivotal in addressing these concerns and setting a roadmap for recovery.






